- Most children under age 3 have flat feet
- Most children develop an arch in standing by around age 6.
- However, about one in five children never develop an arch.
- Flat feet often occur in more than one member of a family.
- Most adults with flat feet have no long-term problems or pain
- Physical examination
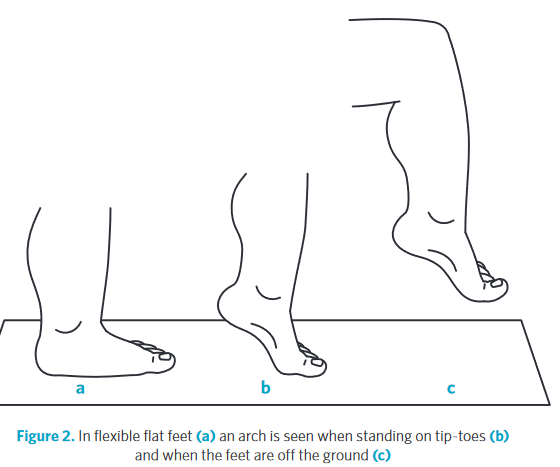
- Ask the child to stand on tip toes.
- If the arch corrects, the foot is flexible (requires no treatment)
- Alternatively, if an arch can be seen in a non-weight-bearing position (e.g. sitting), the foot is flexible (requires no treatment)
- Investigations
- For rigid flatfoot only: weight-bearing X-ray (AP, lateral and oblique)
- GP management
- Reassure parents.
- Most children develop an arch by age six
- The vast majority of patients with flexible flatfoot do not require orthopaedic referral
- Painless flexible flat feet require no treatment.
- Orthotics do not help form an arch and are not recommended
- Refer if
- Rigid flatfoot (arch does not reform
- on tip toe test or in non-weight-bearing)
- Painful flatfoot
- Asymmetry
- Localised tenderness
- Difficulty in functional activities e.g. running, jumping
Related